Custom Neodymium Magnets
Magnetic Hold is a leading manufacturer of custom neodymium magnets. Our team can supply all grades of neodymium magnets, custom shapes, sizes, and coatings.Contact us today for custom-engineered neodymium magnets in any shape and size!
Not only do we offer competitive pricing, but our lead times of 4-6 weeks are convent and reliable for all new and long-time customers.
Some of the most common Neodymium magnets we have provided are N35, N42, N45, N48, N52, and N55. Click below to see our wide selection of grades available for your specific needs.
View Grades & Properties Table
Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) magnets are the most commonly used rare-earth magnets and are made from 3 alloys:
- Neodymium
- Iron
- Boron
Manufacturing of Neodymium Magnets
Neodymium magnets can be manufactured by:
- Sintering
- Compression bonding
- Injection molding
- Extrusion
Magnetizing
- The sintered form holds the highest energy product of up to 55 MGOe
- The bonded form holds a lower energy product of up to 10 MGOe
- The majority of neodymium magnets are anisotropic and can only be magnetized in the direction of orientation
View Magnetism Directions Available
Sizes & Shapes of Neodymium Magnets



Magnetic Hold engineers and manufactures custom neodymium magnets in a variety of shapes and sizes, including:
- Arc
- Bar
- Rod
- Disc
- Horseshoe
- Channel
- Block
- Ring
- Sphere
- Cylinders
- Plugs
Applications of Neodymium Magnets
- Magnetic Separators
- Wind Turbines
- Linear actuators
- Microphone assemblies
- Servo motors
- Tape recorders
- Alternators
- Pacemakers
- DC motors (automotive starters)
- Flow meters
- Headphones
- Magnetic bearings
- Switches
Neodymium Magnet Plating & Coating Options
Neodymium magnets are prone to corrosion in humid environments.
For protective measures for corrosion resistance, Magnetic Hold offers plating and coating options.
Plating:
- Nickel
- Black Nickel
- Chemical Nickel
- Nickel + Epoxy
- Zinc
- Silver
- Gold
Coating:
- Epoxy
- Phosphate
- Phosphate + Parylene
- Phosphate + Teflon
- Plastic
- Nano
Nano Coating: As a water-based coating, it is best suited for magnets that are exposed to salt water.
Magnets with Nano coating showed no signs of corrosion in up to 500 hours of continuous salt spray (5% NaCl, Sodium Chloride) in a controlled environment. Operating temperature of this coating ranges from -40°C to 200°C.
To find out more information, request a quote here through our online form. For custom shapes and sizes, please send a drawing or sketch. If one is not available, we can work with you to create your custom magnets.
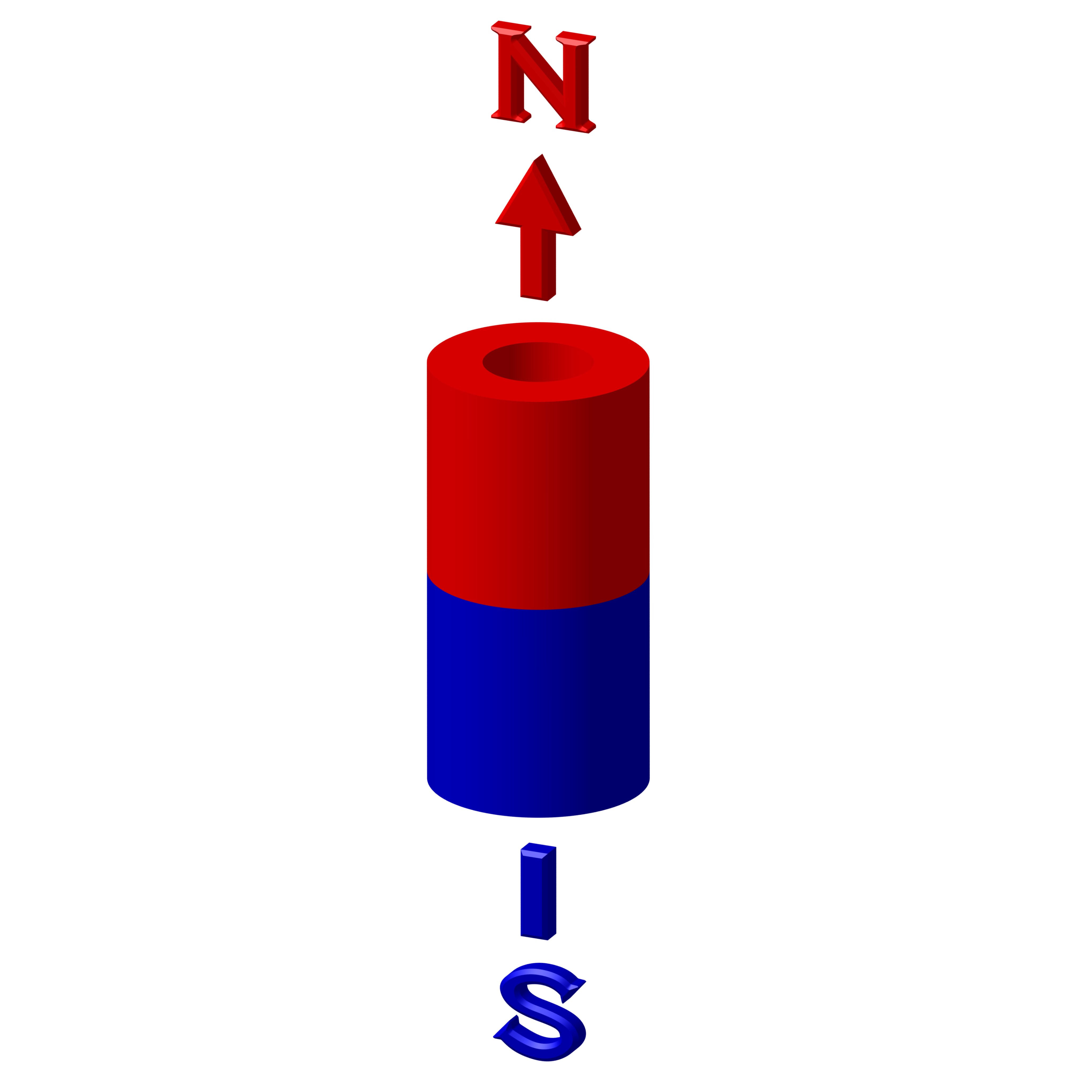
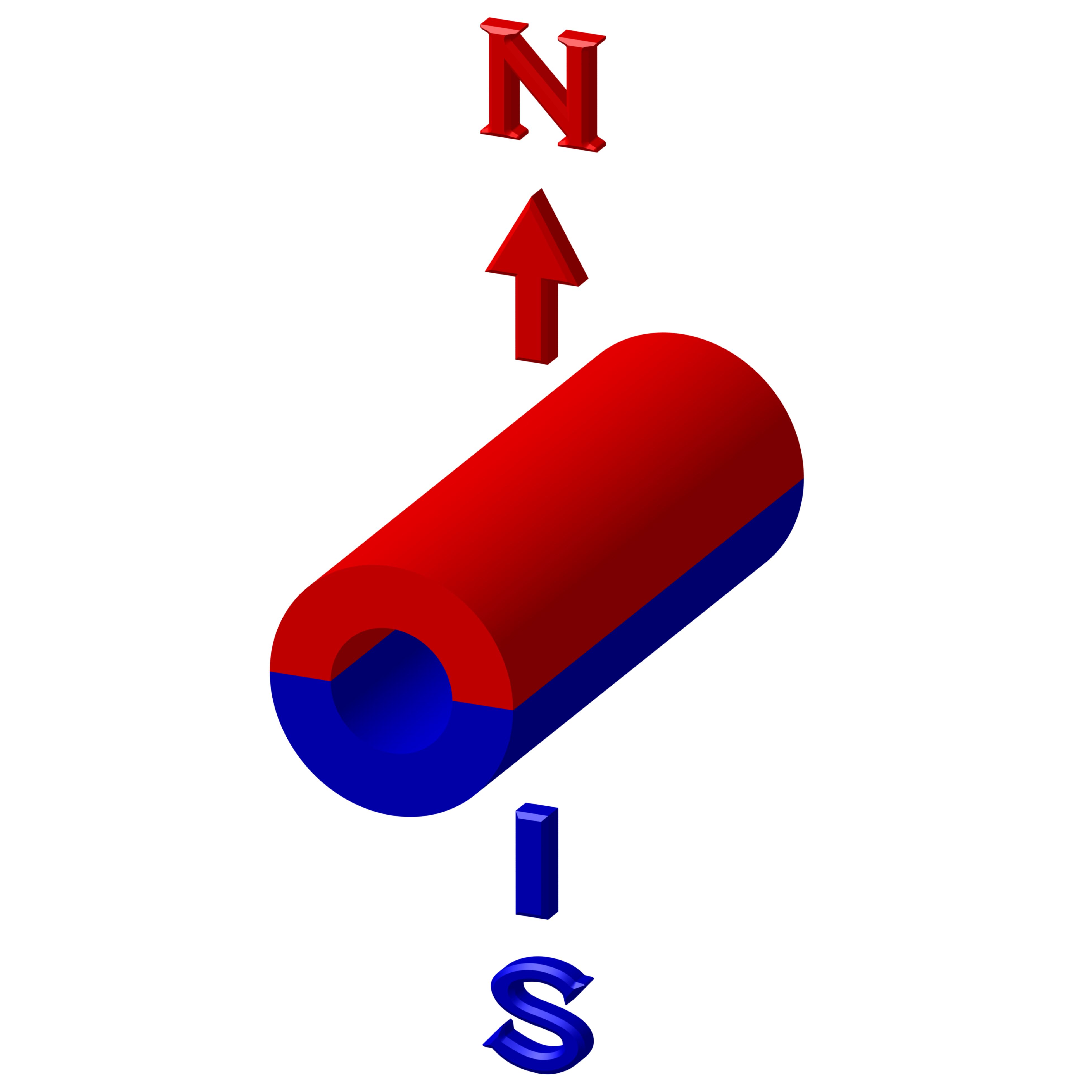
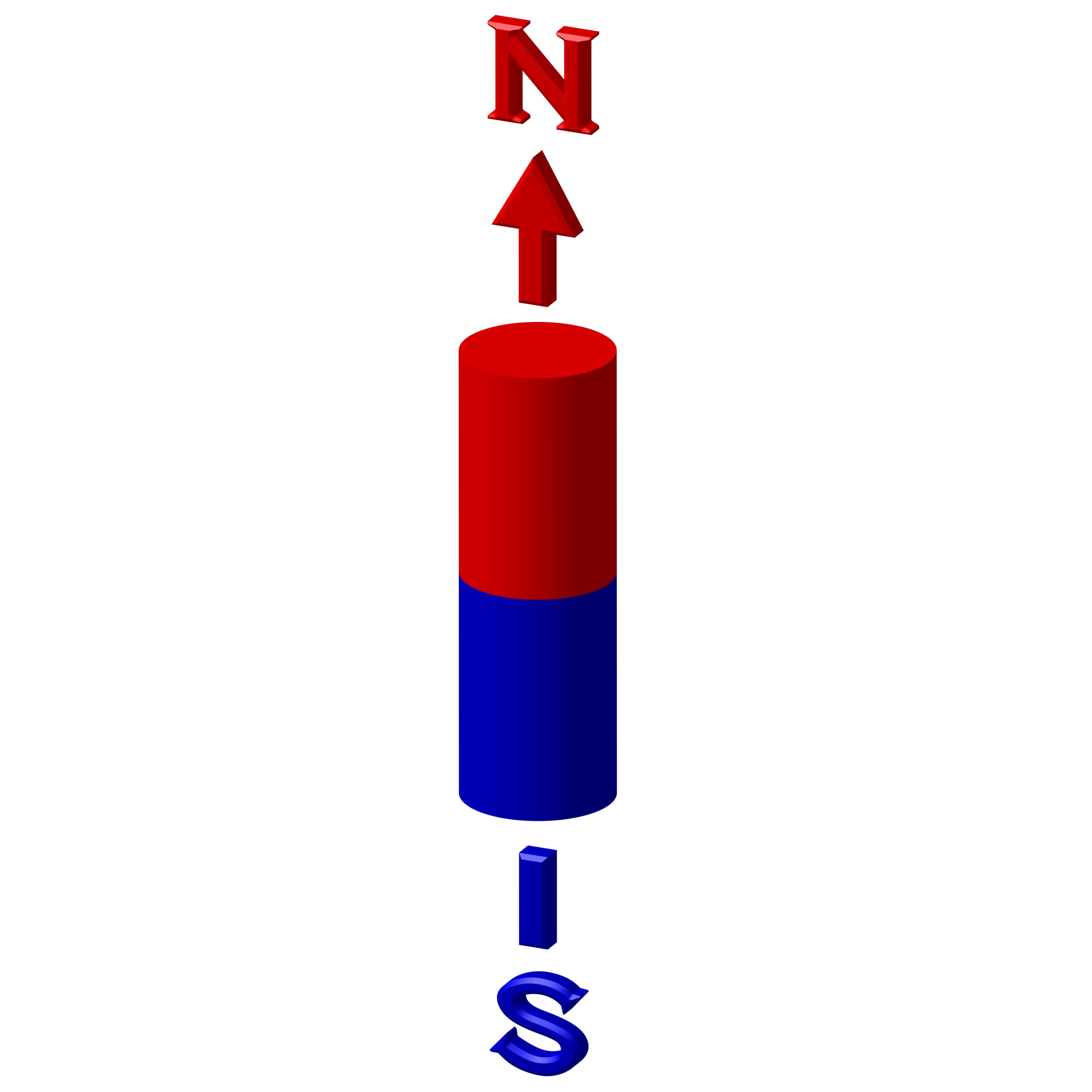
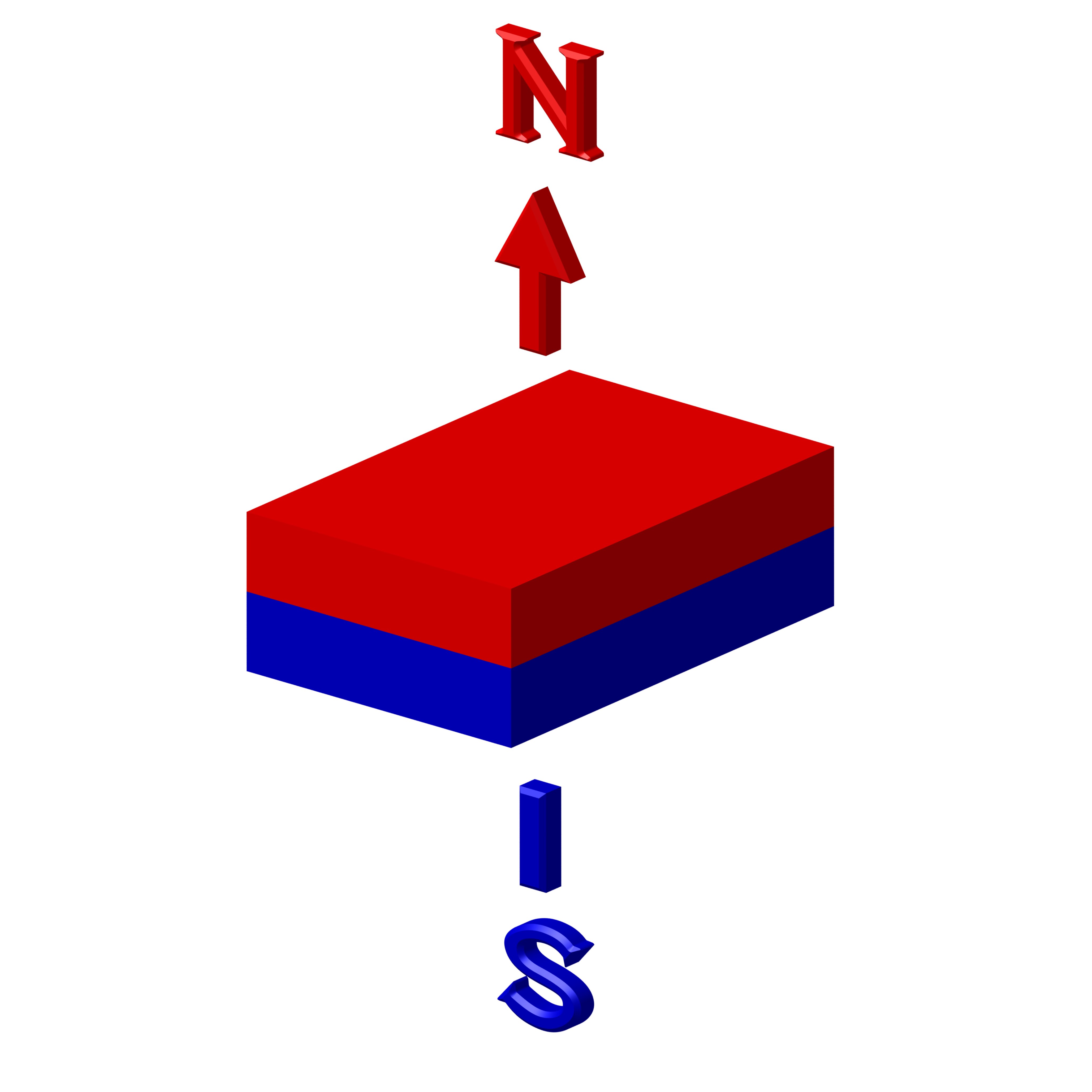
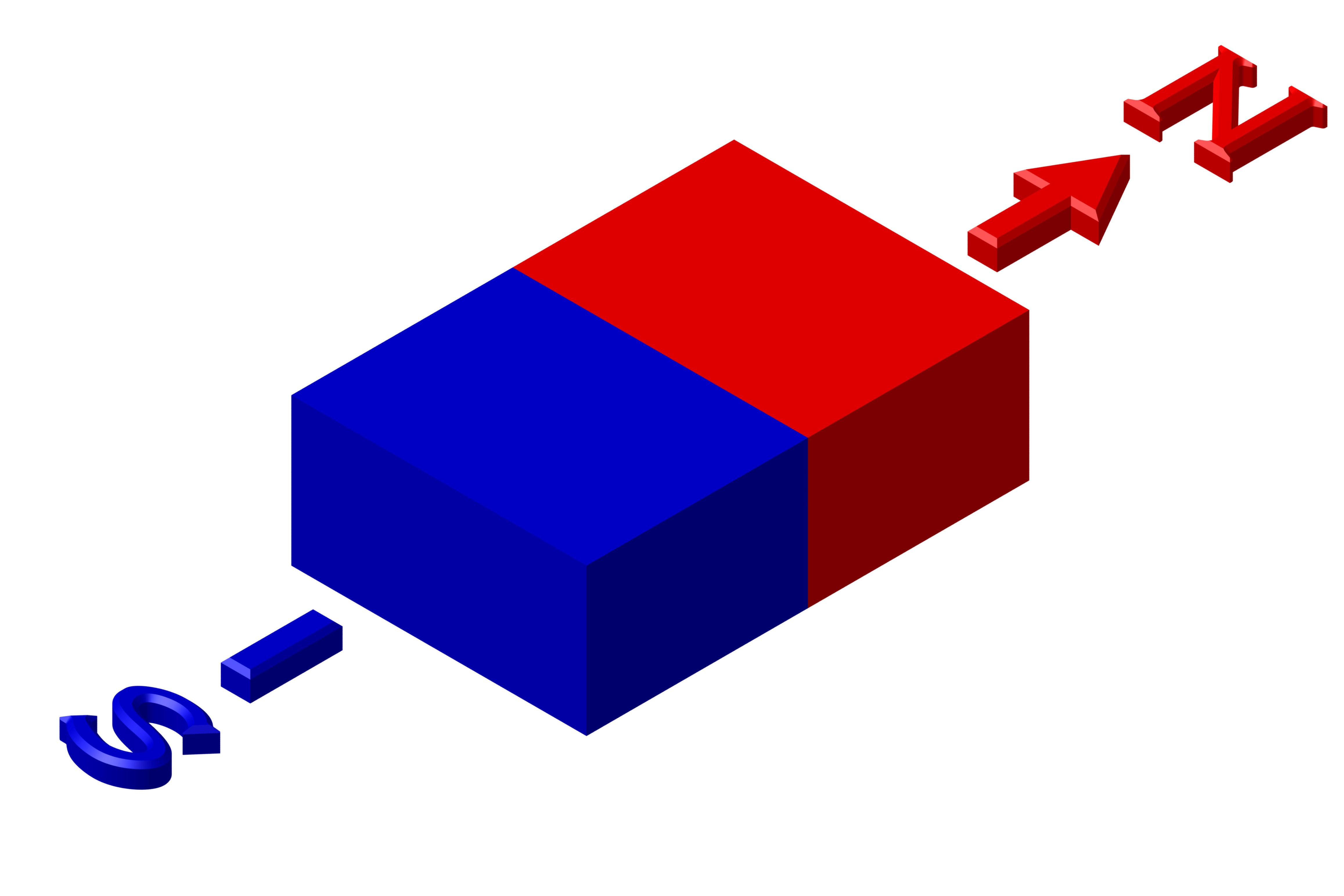
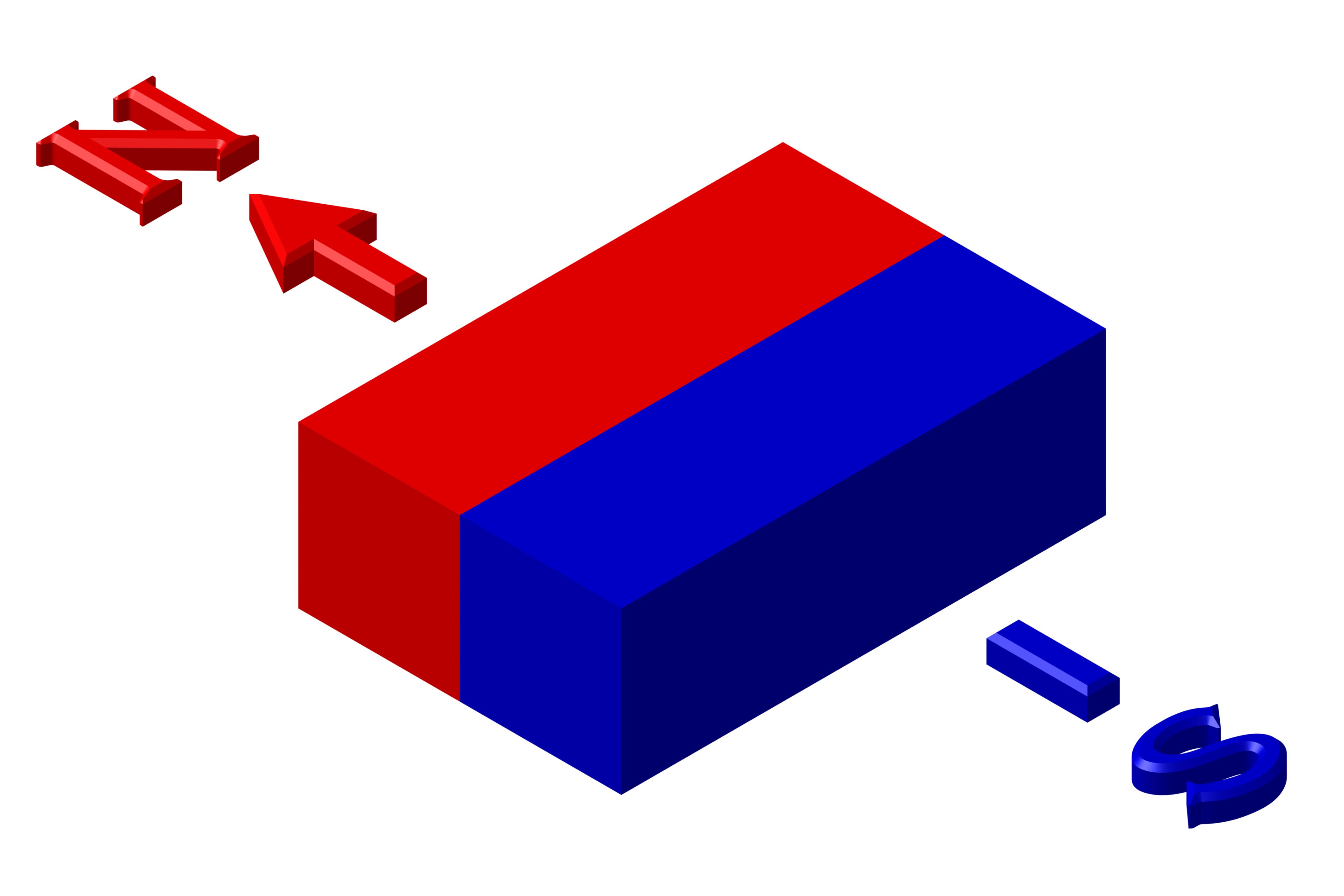
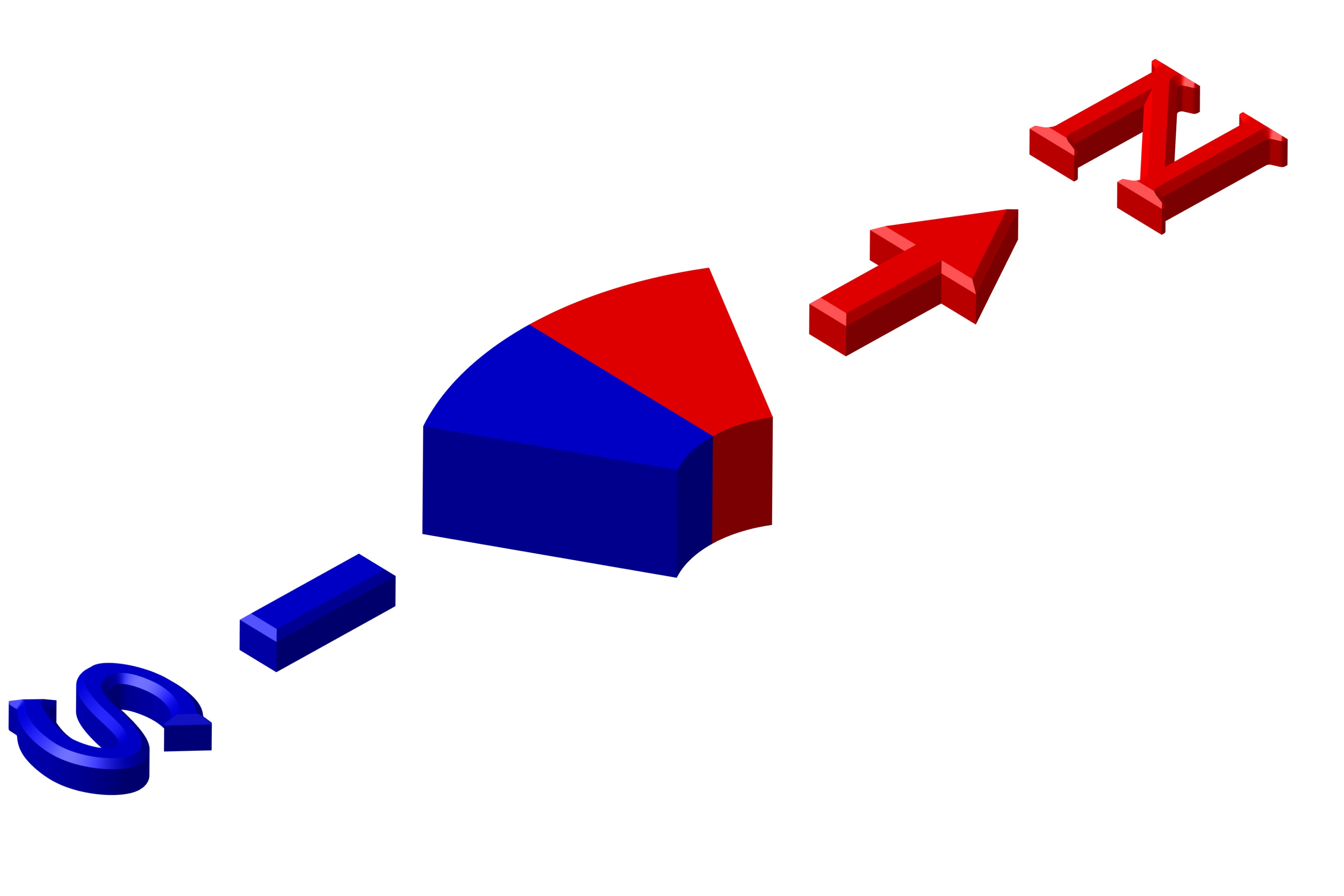
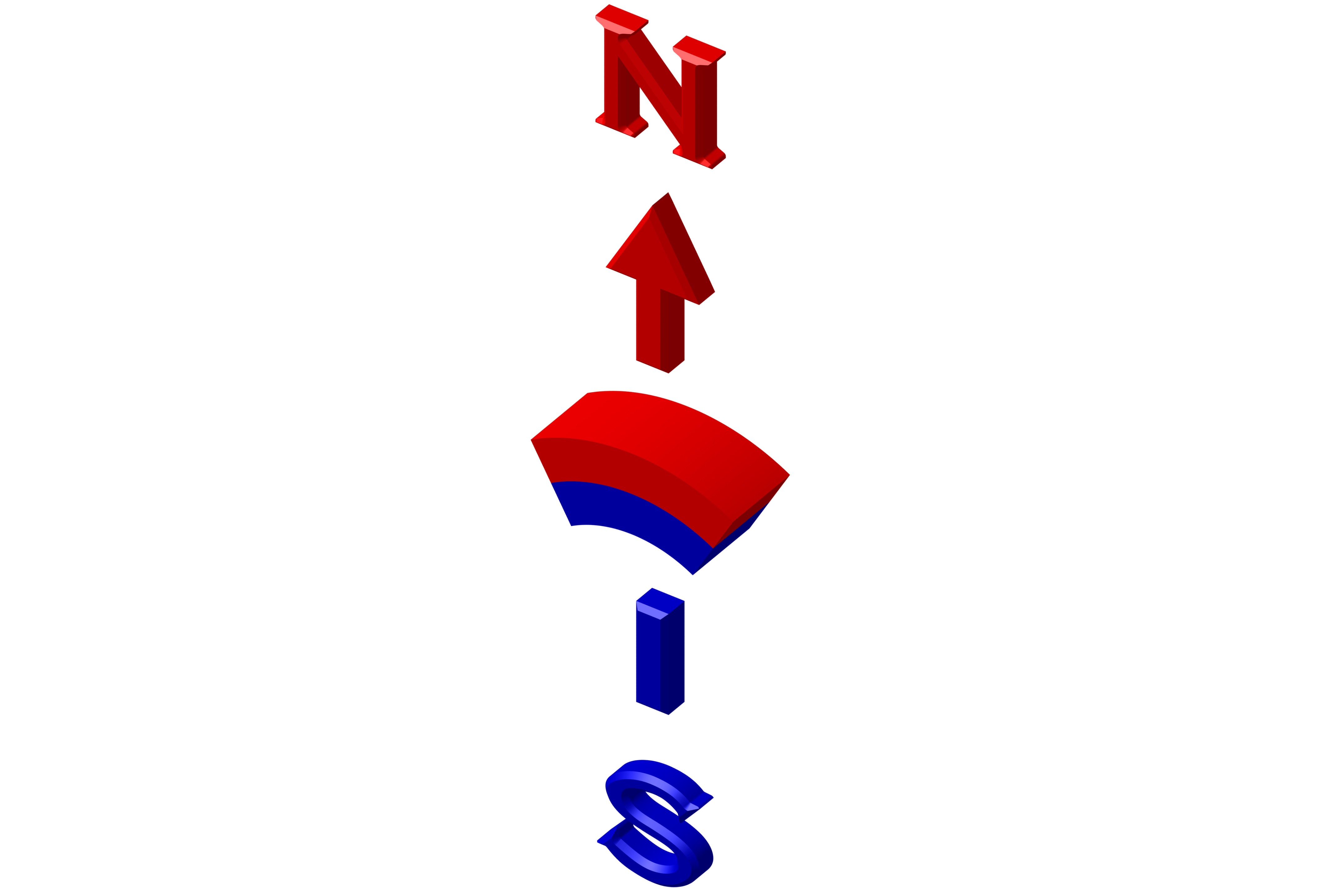
Magnetism Direction Options
We can offer several different magnetization directions, see below schematics. Their availability is limited to size. Magnetization fixture cost may apply for large and custom magnets with magnetization other than what is shown below
The table below offers some guidelines for selecting a grade that will best suit your application.
NEODYMIUM MAGNET GRADES & PROPERTIES
| Grade | Residual Induction Br (max) [KGa] | Max Energy Product BH (max) MGOe | Coercive Force Hcb KOe | Curie Temp. [˚C] | Temp. Coe of Br [%/˚C) | Max. Practical Operating Temp. [˚C] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N30 | 10.8-11.3 | 28-31 | ≥10.0 | 310 | -0.11 | 80 |
| N35 | 11.7-12.2 | 33-36 | ≥10.9 | 310 | -0.11 | 80 |
| N38 | 12.2-12.5 | 36-39 | ≥11.3 | 310 | -0.11 | 80 |
| N40 | 12.5-12.8 | 38-41 | ≥11.4 | 310 | -0.11 | 80 |
| N42 | 12.8-13.2 | 40-43 | ≥11.5 | 310 | -0.11 | 80 |
| N45 | 13.2-13.8 | 43-46 | ≥11.6 | 310 | -0.11 | 80 |
| N48 | 13.8-14.2 | 46-49 | ≥11.6 | 310 | -0.11 | 80 |
| N50 | 14.0-14.5 | 48-51 | ≥10.0 | 310 | -0.11 | 80 |
| N52 | 14.3-14.8 | 50-53 | ≥10.5 | 310 | -0.11 | 80 |
| N55 | 14.5-15.0 | 51-55 | ≥10.5 | 310 | -0.11 | 80 |
| N30M | 10.8-11.3 | 28-31 | ≥10.0 | 310 | -0.11 | 100 |
| N35M | 11.7-12.2 | 33-36 | ≥10.9 | 310 | -0.11 | 100 |
| N38M | 12.2-12.5 | 36-39 | ≥11.3 | 310 | -0.11 | 100 |
| N40M | 12.5-12.8 | 38-41 | ≥11.6 | 310 | -0.11 | 100 |
| N42M | 12.8-13.2 | 40-43 | ≥12.0 | 310 | -0.11 | 100 |
| N45M | 13.2-13.8 | 43-46 | ≥12.5 | 310 | -0.11 | 100 |
| N48M | 13.6-14.3 | 46-49 | ≥12.9 | 310 | -0.11 | 100 |
| N50M | 14.0-14.5 | 47-51 | ≥13.1 | 310 | -0.11 | 100 |
| N52M | 14.2-14.8 | 49-53 | ≥13.1 | 310 | -0.11 | 100 |
| N30H | 10.8-11.3 | 28-31 | ≥10.0 | 330 | -0.11 | 120 |
| N35H | 11.7-12.2 | 33-36 | ≥10.9 | 330 | -0.11 | 120 |
| N38H | 12.2-12.5 | 36-39 | ≥11.3 | 330 | -0.11 | 120 |
| N40H | 12.5-12.8 | 38-41 | ≥11.6 | 330 | -0.11 | 120 |
| N42H | 12.8-13.2 | 40-43 | ≥12.0 | 330 | -0.11 | 120 |
| N45H | 13.2-13.8 | 43-46 | ≥12.1 | 330 | -0.11 | 120 |
| N48H | 13.7-14.3 | 46-49 | ≥12.5 | 330 | -0.11 | 120 |
| N50H | 14.0-14.5 | 47-51 | ≥12.8 | 330 | -0.11 | 120 |
| N52H | 14.2-14.8 | 50-54 | ≥12.8 | 330 | -0.11 | 120 |
| N30SH | 10.8-11,3 | 28-31 | ≥10.1 | 340 | -0.11 | 150 |
| N35SH | 11.7-12.2 | 33-36 | ≥11.0 | 340 | -0.11 | 150 |
| N38SH | 12.2-12.5 | 36-39 | ≥11.4 | 340 | -0.11 | 150 |
| N40SH | 12.5-12.8 | 38-41 | ≥11.8 | 340 | -0.11 | 150 |
| N42SH | 12.8-13.2 | 40-43 | ≥12.4 | 340 | -0.11 | 150 |
| N45SH | 13.2-13.8 | 43-46 | ≥12.6 | 340 | -0.11 | 150 |
| N48SH | 13.6-14.0 | 43-47 | ≥11.5 | 340 | -0.11 | 150 |
| N50SH | 13.9-14.2 | 48-51 | ≥13.1 | 340 | -0.11 | 150 |
| N30UH | 10.8-11.3 | 28-31 | ≥10.2 | 350 | -0.11 | 180 |
| N35UH | 11.8-12.2 | 33-36 | ≥10.8 | 350 | -0.11 | 180 |
| N38UH | 12.2-12.5 | 36-39 | ≥11.0 | 350 | -0.11 | 180 |
| N40UH | 12.5-12.8 | 38-41 | ≥11.3 | 350 | -0.11 | 180 |
| N42UH | 12.8-13.5 | 40-43 | ≥11.0 | 350 | -0.11 | 180 |
| N45UH | 13.2-13.8 | 42-46 | ≥11.0 | 350 | -0.11 | 180 |
| N48UH | 13.6-14.0 | 46-49 | ≥12.9 | 350 | -0.11 | 180 |
| N30EH | 10.8-11.3 | 28-31 | ≥10.2 | 360 | -0.11 | 200 |
| N35EH | 11.7-12.2 | 33-36 | ≥11.0 | 360 | -0.11 | 200 |
| N38EH | 12.2-12.5 | 36-39 | ≥11.3 | 360 | -0.11 | 200 |
| N40EH | 12.8-12.8 | 38-41 | ≥11.8 | 360 | -0.11 | 200 |
| N42EH | 12.8-13.2 | 40-44 | ≥12.5 | 360 | -0.11 | 200 |
| N45EH | 13.2-13.6 | 43-46 | ≥12.5 | 360 | -0.11 | 200 |
| N30AH | 10.8-11.3 | 28-31 | ≥10.2 | 360 | -0.11 | 220 |
| N35AH | 11.7-12.1 | 33-37 | ≥11.0 | 360 | -0.11 | 220 |
Br: Residual Induction
Gs: Gauss
Hc: Coercive Force
Oe: Oersted
˚C: Degree Celcius
MGOe: Mega Gauss Oersted
Standard Tolerances (inches);
All shapes and sizes (±0.005)
Caution!
Extreme caution must be taken when working with rare earth magnets. Magnets larger than a few centimeters are strong enough to cause injuries to body parts pinched between two magnets, or a magnet and a metal surface, even causing broken bones. Magnets allowed to get too close to each other can strike one another with force to chip and shatter the brittle material, and the flying chips can cause injuries.